
" +" is taken as default sign if none is specified. A valid " dd " number of days can be any number in the range of 0– 32768. Can also select files with a last modified date greater than or equal to ( +) the current date plus " dd" days, or less than or equal to ( -) the current date minus " dd" days. Selects files with a last modified date greater than or equal to ( +), or less than or equal to ( -), the specified date using the " MM / DD / YYYY" format. (For a detailed explanation, see this thread on Stack Overflow.) All commands should be preceded with " cmd /c," although it can be omitted if the command is an external command which requires no arguments. To include special characters in the command line, use the hexadecimal code for the character in 0x HH format (e.g., 0x09 for the tab character). If the file has more than one extension, only the trailing extension is – returns the full path of the file, including the file – returns the relative path of the – returns TRUE if a file type is a directory, and FALSE for – returns the size of the file in – returns the last modified date of the – returns the last modified time of the file. If the file has multiple extensions, e.g.,, only the trailing extension is truncated, e.g., a result of – returns only the extension of the file.
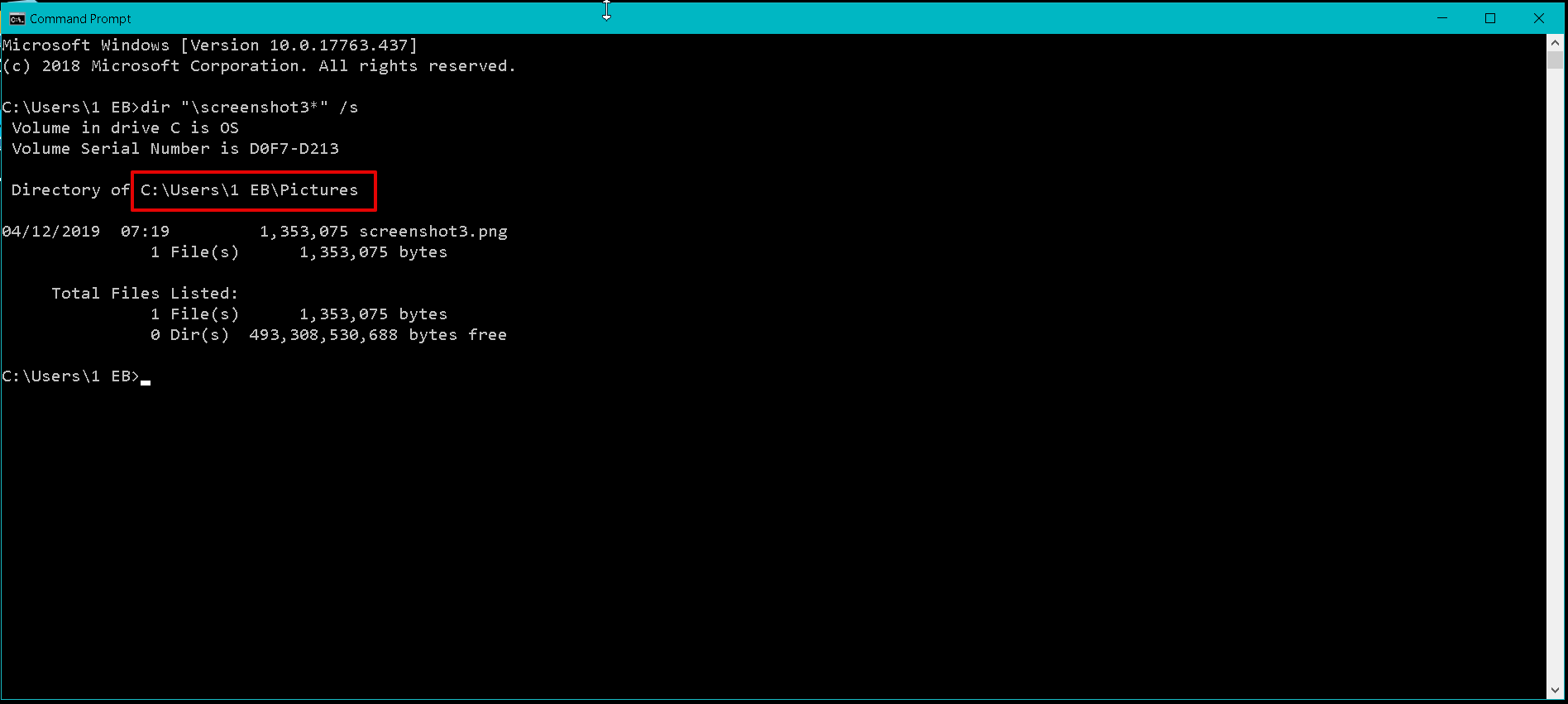
The following variables can be used in the command – returns the name of the file, with no path – returns the file name without extension. The default command is " cmd /c echo which displays the name of the file. Recurse into subdirectories, as with " DIR /S".Įxecute command on each file where command is a command string, enclosed in double quotes. The default search mask is "*" (an asterisk), which matches all files and directories. Searches files (and directories, if the /S option is specified) whose name matches a search mask searchmask, which may contain wildcards. If not specified, the current directory (.

Its executable file is installed at %WINDIR%/System32/forfiles.exe. It's also available as part of Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, and Windows 11. Beginning with Windows Vista, it was included in the standard Windows operating system.

The forfiles command was first introduced as an optional component of Windows NT.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
